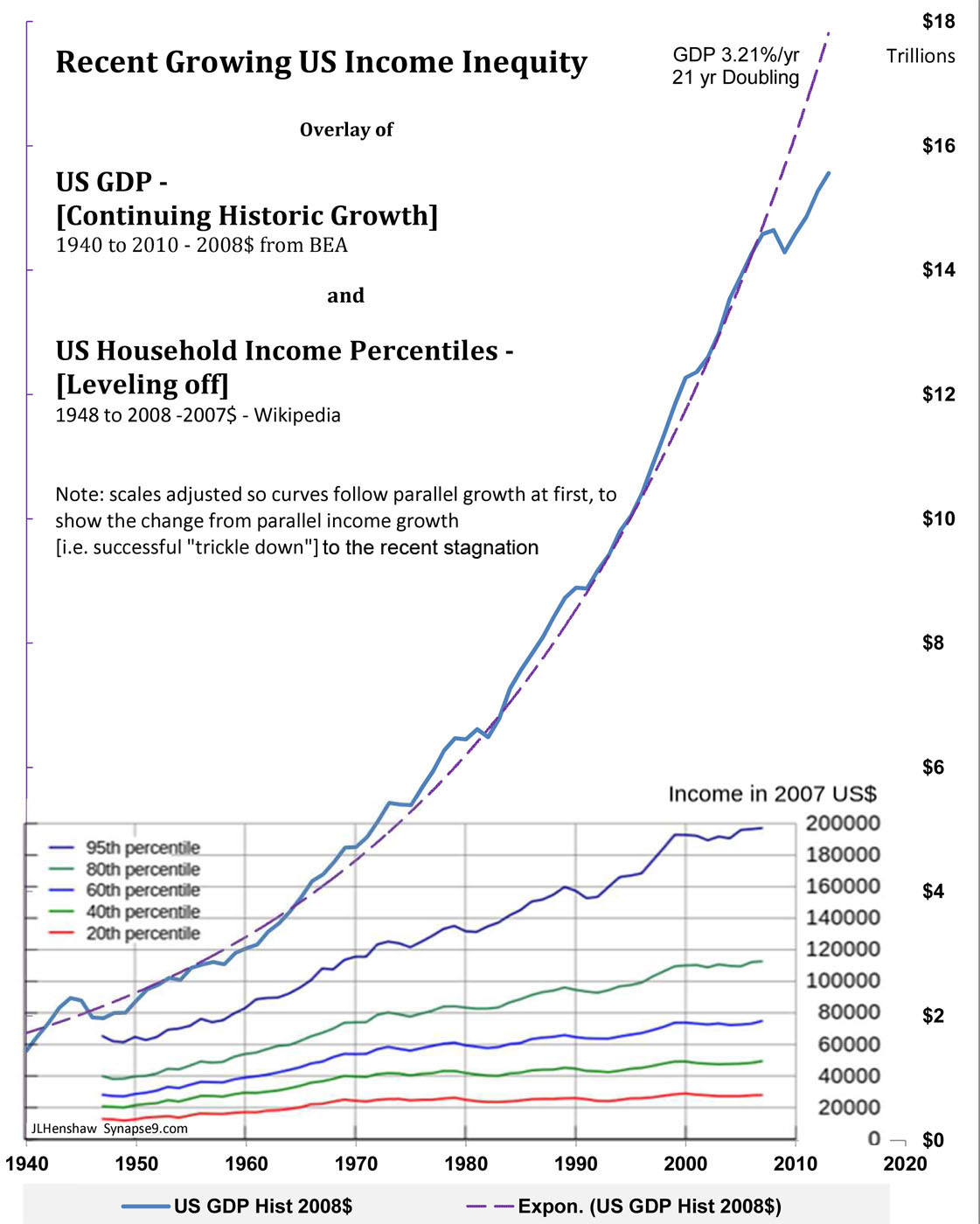
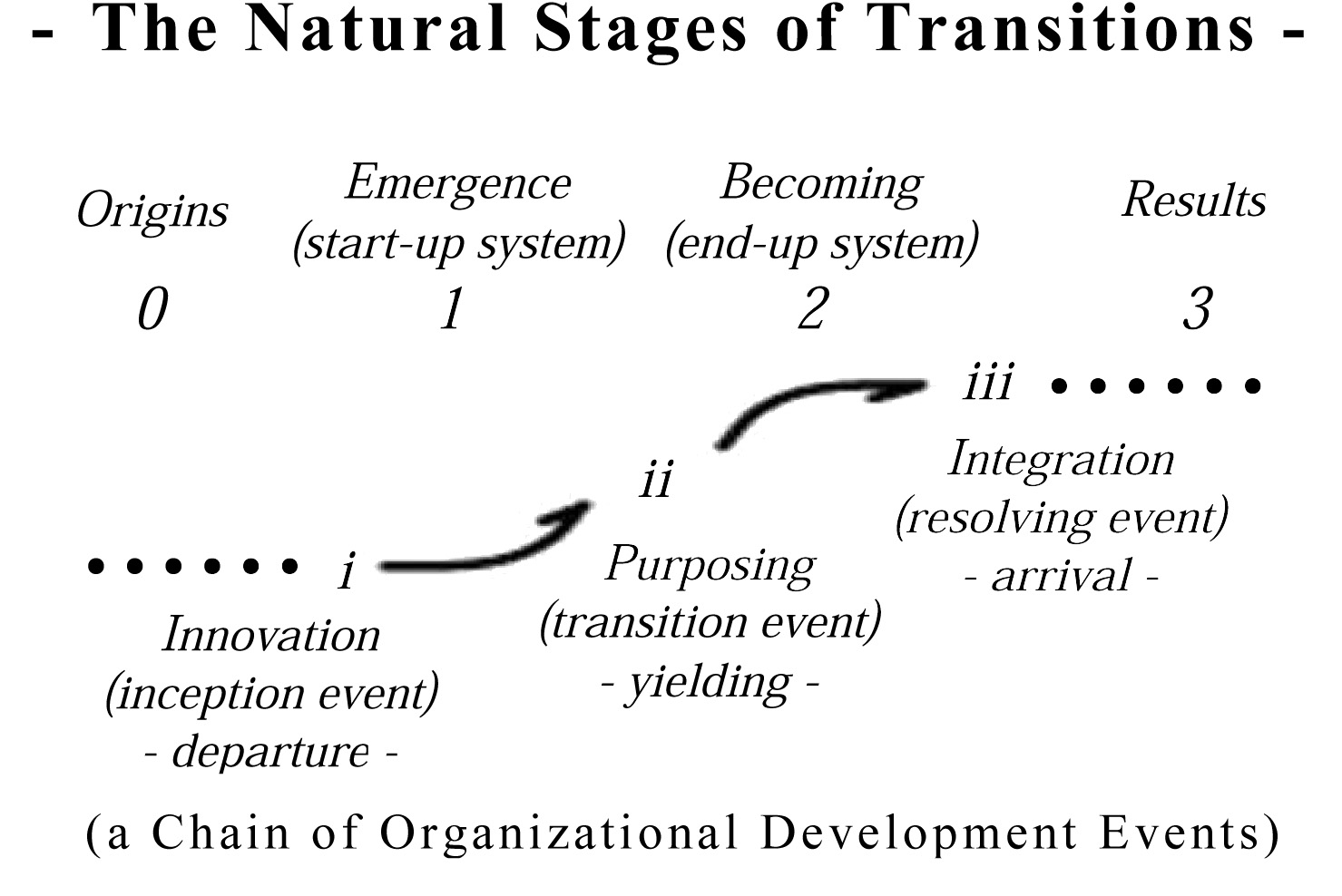
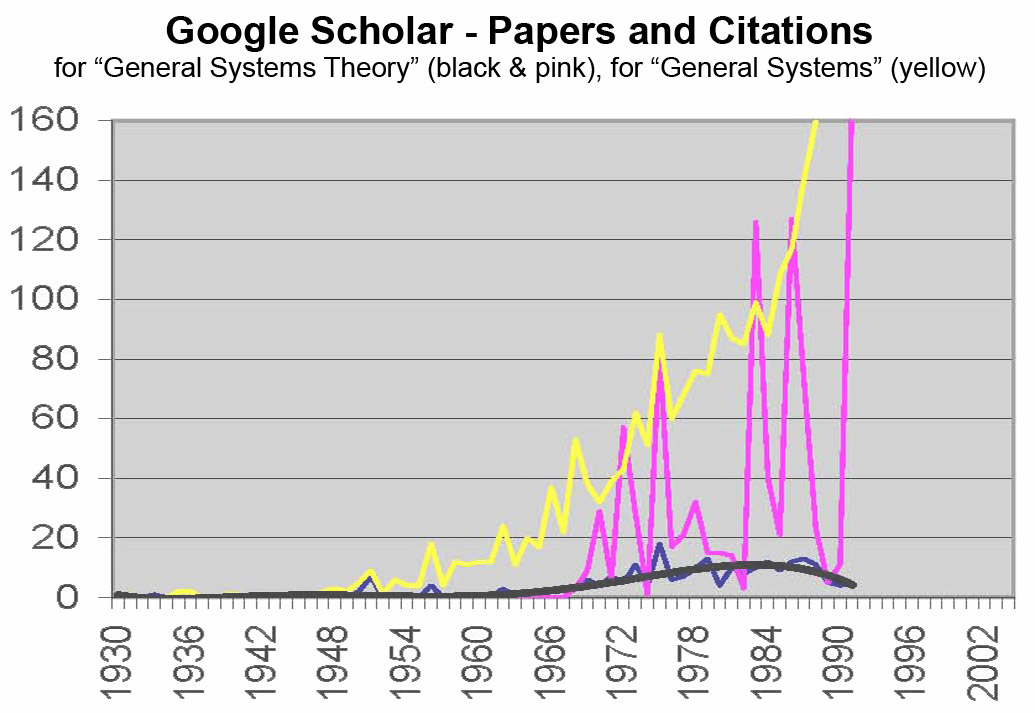
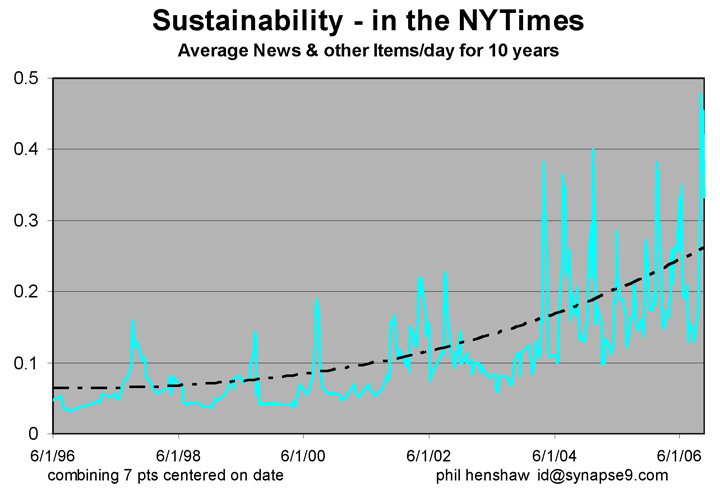
This post is a section of my report titled “Approaching 30 days from the 40th Anniversary” on attending the quite exciting 2012 40th Anniversary meeting on the Meadows and Randers authored Club of Rome “Limits to Growth” study. The excerpt is on the deep reasons why the science, as solid as it still seems to be, isn’t widely accepted. Science is still struggling to find a comfortable way to discuss natural systems whose innovative systems are housed internally, and so largely hidden from view.
___________
I think the real reason the public as well as most of the scientific community is largely ignoring the rather well established hard limits to growth, is that it presents the scientific community a new problem it hasn’t yet learn how to deal with. It has yet to find a good way to make sense of self-designing and self-managing systems, like weather systems, cultures and economies, that have working designs that are hidden internally, displaying organization much too complex and localized to be determined by external forces.
Science is built around identifying how one thing controls another,
not how to study the patterns of uncontrolled systems and how they became designed to work by themselves.
So science is naturally somewhat lost in discussing how they work, having no model for what are better described as “opportunistic” than “deterministic” systems. Though both climate and economies display highly inventive systems, they do still necessarily operate within what traditional science can define as their natural bounds. Climate is still fundamentally a complex pressure-temperature behavior, of unchanging deterministic processes following fixed laws of science.
Economies though, are able to be far more creative, and move the boundaries of what is possible by innovative design, much further than the push and pull forces of the weather can. It has given traditional science very little to anchor reliable theory on, except as in the Limits to Growth study, fixing boundary conditions and experimenting with multiple options. Still, because economies do display deeply creative behavior, constantly inventing new ways to use energy as a normal rule, that natural science still lacks a widely accepted way to study them as natural systems, adds uncertainty for others to what anyone might say about them.
Constantly inventing new organization is just what natural systems ‘do’. It lets economies as well as ecologies create new kinds of organization and uses for their energy resources, making formerly useless things highly profitable often enough. Using the profits as returns on energy investment to grow by building more innovations. It’s complicated by not being a ‘numeric’ process, though we can see it through our measures. It’s an “organizational process”, of fitting complementary parts together, more amenable to study as a “pattern language” of “design elements” than equations.
The rigid limits of any mode of productivity still do exist, of course, but as limits of the organizational processes science has yet to find a way to study. Those limits are still determined by the earth and the organization of the internal and external systems that any innovation depends on, but with each new innovation there are new unknown limits. It leaves a stubborn problem for traditional scientific prediction. What seems to work better is a language of observing such systems to see when their own organization is being stretched.
That big problem for science also makes a big and very fascinating subject of study, that science has quite generally not realized is there, having avoided the study of self-designing and managing systems in general. Self-designing ans managing systems not only seem to develop by themselves, but to have their “works” hidden internally within the boundaries of their design, as an individual system maintaining internal organization for responding to external systems, like we see in living systems as a special case in point. Continue reading Can science learn to read “pattern language”…?